Why Beta Matters More Than You Think
you’re building the perfect investment portfolio. You’ve got your eye on a mix of stocks—some stable giants, others wild high-flyers. But how do you measure their risk? How do you know if they’ll soar or crash when the market takes a turn? Enter beta for stocks, a financial metric that’s like a crystal ball for gauging volatility. As a financial specialist, I’ve seen countless investors overlook beta, only to regret it later. Today, I’ll unravel this powerhouse concept, show you how it works, and reveal why our free Portfolio Analyzer Tool on our website is your secret weapon for mastering it.
Beta isn’t just a number—it’s your guide to balancing risk and reward. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a newbie dipping your toes into the stock market, understanding beta can transform your strategy. In this article, we’ll explore the beta for stocks definition, dig into what the beta value means, answer whether beta equals market risk, and even walk you through a stock beta calculation. Plus, I’ll sprinkle in real-world examples and actionable insights. Ready to level up your investing game? Let’s get started.
Beta for Stocks Definition: What’s It All About?
Beta measures a stock’s volatility compared to the overall market. Think of it as a pulse check—how much does a stock jump or dip when the market moves? The market, often represented by an index like the S&P 500, has a beta of 1.0. If a stock’s beta is higher than 1.0, it’s more volatile than the market. Below 1.0? It’s less volatile. Simple, yet powerful.
For example, a stock with a beta of 1.5 tends to amplify market movements by 50%. If the S&P 500 climbs 10%, that stock might leap 15%. On the flip side, a beta of 0.5 means it’s steadier—less swayed by market swings. This metric stems from the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), a cornerstone of modern finance that ties risk to expected returns.
Why does this matter? Because beta helps you match your investments to your risk appetite. Love the thrill of big wins (and potential losses)? High-beta stocks might be your jam. Prefer steady growth without the rollercoaster? Low-beta stocks could be your sweet spot. Our free Portfolio Analyzer Tool crunches these numbers for you, spotlighting how beta shapes your holdings. No guesswork—just results.
What Is Beta Value in Stocks? Decoding the Numbers
Let’s break it down further. The beta value in stocks isn’t some arcane code—it’s a practical snapshot of risk. Here’s what different beta values signal:
- Beta > 1 (High Beta): These stocks are the daredevils. Tech giants like Tesla (beta often around 1.8–2.0) dance to a wilder tune than the market. When the economy booms, they skyrocket. During downturns? Brace for a steeper fall.
- Beta = 1: These mirror the market’s rhythm. Think of a stock like Coca-Cola—stable, predictable, marching in lockstep with the S&P 500.
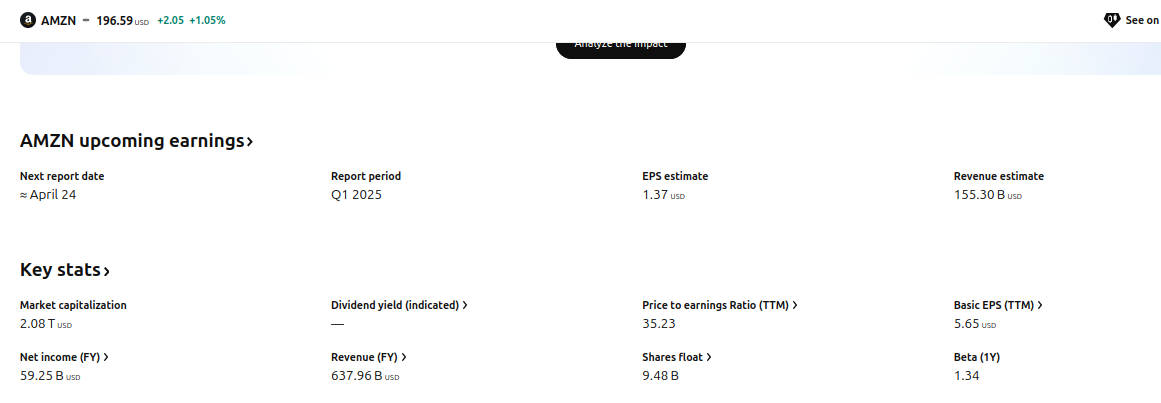
- Beta < 1 (Low Beta): The calm-before-the-storm crew. Utility companies, with betas often around 0.3–0.7, shrug off market chaos. They’re your portfolio’s anchors.
- Beta = 0: No correlation to the market. Rare, but think cash or fixed-income assets.
- Negative Beta: A unicorn! Stocks like gold miners sometimes dip when the market rises (and vice versa), offering a hedge.
Here’s the kicker: beta isn’t static. It shifts with market conditions, company performance, and sector trends. That’s why our Portfolio Analyzer Tool updates beta in real time, giving you a dynamic view of your investments. Curious about your stocks’ beta values? Plug them into our tool—it’s free, fast, and freakishly accurate.
Is Beta Market Risk? The Truth Revealed
Does beta equal market risk? Yes—and no. Beta captures systematic risk, the volatility tied to broad market movements. If the economy tanks or interest rates spike, beta tells you how your stock might react. But it’s not the whole story.
Systematic risk differs from unsystematic risk, which is company-specific—think scandals, lawsuits, or product flops. Beta ignores these. A stock with a low beta might still crater if its CEO gets caught in a fraud. So, while beta is a stellar gauge of market-driven risk, it’s not a catch-all.
Consider this: two stocks might share a beta of 1.2, but one’s a biotech startup, the other a mature retailer. The biotech’s unsystematic risk (like a failed drug trial) could tank it, while the retailer chugs along. Beta keeps you focused on the market’s pulse, but pairing it with diversification tames the wildcards. Our Portfolio Analyzer Tool doesn’t just spit out beta—it maps your portfolio’s risk holistically. Try it—see the bigger picture.
Stock Beta Calculation: How Do the Pros Do It?
Want to geek out on the math? Calculating beta isn’t rocket science, but it does require some elbow grease. Here’s the step-by-step:
- Gather Data: Pick your stock and a market index (e.g., S&P 500). Collect daily or monthly returns for both over a set period—say, 5 years.
- Calculate Returns: For each period, compute the percentage change. Stock return = (New Price – Old Price) / Old Price. Same for the index.
- Find Covariance and Variance: Covariance measures how the stock and market move together. Variance tracks the market’s volatility alone.
- Apply the Formula: Beta = Covariance (Stock Returns, Market Returns) / Variance (Market Returns).
- Interpret: Voilà—your beta is born!
A Real-World Example
Let’s crunch it. Say Stock X’s returns over 5 months are [2%, -1%, 3%, 4%, -2%], and the S&P 500’s are [1%, 0%, 2%, 3%, -1%]. Using a spreadsheet (or our tool!), you’d:
- Covariance = 0.0025 (stock and market move in tandem).
- Variance = 0.002 (market’s spread).
- Beta = 0.0025 / 0.002 = 1.25.
Stock X is 25% more volatile than the market. Simple, right? But who’s got time for spreadsheets? Our Portfolio Analyzer Tool does this heavy lifting instantly—and it’s free. No PhD required.
Why Beta Is Your Portfolio’s MVP
Beta isn’t just trivia—it’s a game-changer. It helps you:
- Balance Risk: Mix high- and low-beta stocks to match your goals.
- Spot Opportunities: High-beta stocks shine in bull markets; low-beta thrives in bearish times.
- Stress-Test: See how your portfolio holds up when the market flips.
Our Portfolio Analyzer Tool takes this further. Enter your holdings, and it spits out a beta-weighted risk profile. You’ll know exactly where you stand—and how to tweak it. Free, user-friendly, and built by financial pros—why wouldn’t you use it?
H2: FAQ Section: Your Beta Questions Answered
H3: What’s a Good Beta for a Stock?
It depends! Aggressive investors might chase betas above 1.5 for growth. Conservative folks might stick to 0.5–1.0 for stability. Check your risk tolerance with our tool.
H3: Can Beta Change Over Time?
Absolutely. A company’s beta evolves with its business, debt, or sector shifts. Regular updates via our analyzer keep you ahead.
H3: Is a Negative Beta Bad?
Not at all—it’s a hedge! Negative-beta assets like gold can offset losses when stocks tank.
H3: How Often Should I Check My Portfolio’s Beta?
Monthly or after big market moves. Our tool makes it a breeze—try it now!
Conclusion: Take Control with Beta and Our Free Tool
Beta for stocks isn’t just a metric—it’s your roadmap to smarter investing. From defining risk to calculating volatility, it empowers you to build a portfolio that sings. But with our free Portfolio Analyzer Tool, you don’t need to wrestle with the complexity alone. Plug in your stocks, decode their betas, and watch your strategy sharpen.
So, what’s your next move? Test your portfolio’s pulse today. Visit our website, fire up the tool, and unlock insights that Wall Street pros swear by—all without spending a dime. Your financial future deserves it.

